HELLO WORLD
Welcome to the world of Java programming!
Programming languages enable humans to write instructions that a computer can perform. With precise instructions, computers coordinate applications and systems that run the modern world.
Sun Microsystems released the Java programming language in 1995. Java is known for being simple, portable, secure, and robust. Though it was released over twenty years ago, Java remains one of the most popular programming languages today.
One reason people love Java is the Java Virtual Machine, which ensures the same Java code can be run on different operating systems and platforms. Sun Microsystems’ slogan for Java was “write once, run everywhere”.
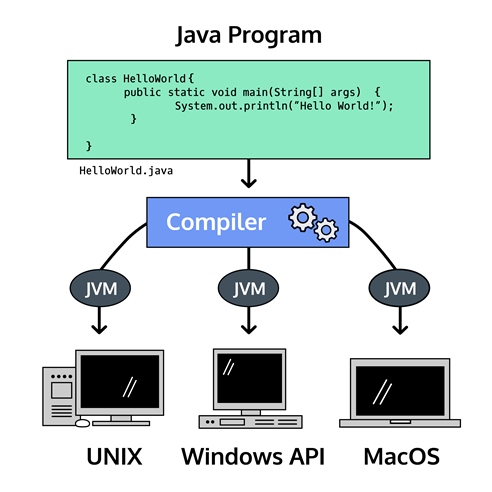
Programming languages are composed of syntax, the specific instructions which Java understands. We write syntax in files to create programs, which are executed by the computer to perform the desired task.
Let’s start with the universal greeting for a programming language. We’ll explore the syntax in the next exercise.
- You’re looking at a computer program written in Java. Run the code in the text editor to see what is printed to the screen.
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}

